
Share:
Can artificial intelligence serve as an inventor? How Might AI as Inventors Affect Our Traditional Understanding of Inventorship? Do the benefits of recognizing AI as an inventor outweigh the concerns and challenges?
The recent Thaler v. Vidal case aroused debate on whether or what can be considered an inventor. The lawsuit concerned an AI system named “Dabus” that invented two new products: a food container and a blinking light. However, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) rejected the patent applications, claiming that only humans can be named inventors. This case serves as an important focus point for discussing AI inventors and their acknowledgment in the patent system.
This lawsuit brought AI’s status as innovators to the forefront. Let us delve further into this debate.
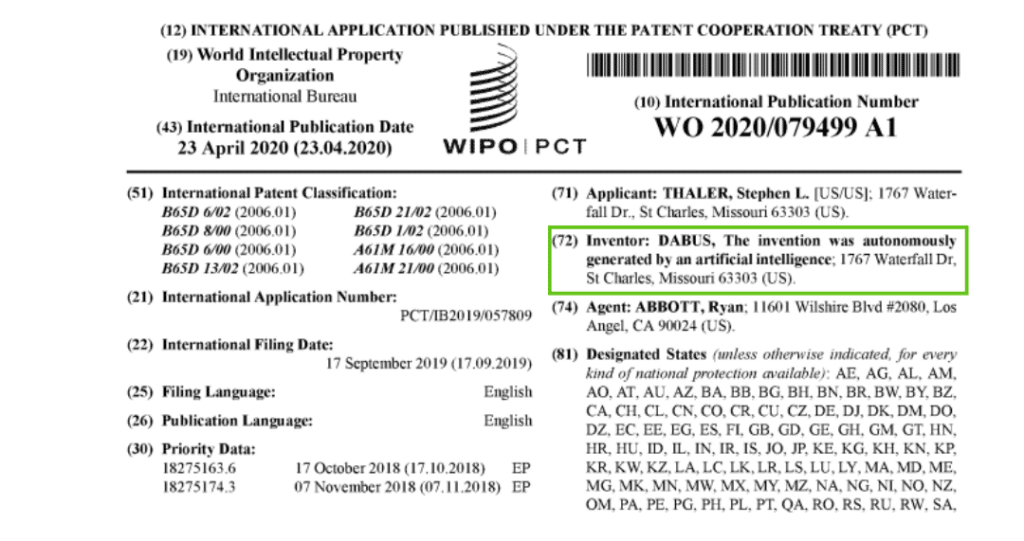
Figure 1: Patent Application
Current patent laws and their limitations in accommodating AI inventorship
The current patent laws were crafted with human inventors in mind, creating a legal conundrum when faced with inventions generated by AI. The Thaler case, featuring the AI system “DABUS” autonomously generating inventions, prompted questions about the traditional definition of an inventor. Patent offices and courts globally grappled with determining the legal status of AI as an inventor, highlighting the shortcomings of existing laws in adapting to this paradigm shift. Some argue that invention is a uniquely human endeavor involving creativity, decision-making, and an understanding of ethical implications. Granting AI inventor rights raises concerns about accountability, liability, and the potential misuse of intellectual property. Many argued that striking a balance between fostering innovation and addressing accountability and ethical implications is crucial.
Advantages held by AI in the role of an Inventor
The rise of LLMs and generative AI combines the originally held capability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate predictions with human-like logical reasoning and interpretation over volumes of text. Unlike human inventors, AI can learn faster and contemplate various permutations and combinations over a wider range of datapoints. Additionally, AI’s computational power enables it to generate inventive solutions to complex problems, surpassing traditional human approaches. AI can dodge traditional approaches and discover unique ideas transforming traditional ways of invention thinking process. So, when we talk about AI-generated inventions, we’re not just talking about technology – we’re talking about a powerhouse of creativity, problem-solving, and game-changing potential.
Weaknesses of AI-generated inventions
The patent system offers a period of exclusivity as an incentive to inventors, assuring them that their hard work won’t be immediately copied giving them the potential for financial return on their investment of time, resources, and intellect. Unlike human inventors, AI doesn’t seek recognition, financial gains, or societal acknowledgment. AI lacks the intrinsic human qualities that respond to the patent system’s incentives, and this can be reflected in the quality of inventions generated by AI. Hence, AI’s limited contextual understanding and absence of intuition hinder its adaptability to unforeseen situations and complex problem-solving scenarios.
Since AI-generated outputs rely on training data, they often replicate preexisting concepts and lack innovation and originality. Furthermore, biases in the data can also be perpetuated, raising ethical concerns. The need for human oversight in ethical considerations, addressing limitations, and interpreting results underscores the reliance on human judgment and expertise. Addressing these weaknesses is crucial for responsible technological development.
Recent Developments
Some jurisdictions, like the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and the European Patent Office (EPO), have rejected AI inventorship, emphasizing the requirement for a natural person to be named as the inventor. However, the Australian and South African patent offices have taken a more progressive approach, accepting AI-generated inventions. These inconsistencies underscore the urgent need for a standardized, globally accepted framework for AI inventorship.
As AI continues to advance, it also becomes necessary to update patent laws to ensure that they are aligned with the rapid progress of technology. The old framework of patent laws was established largely for human inventors, creating controversy over the ownership and rights of AI-generated creations. Recognizing the contributions of AI inventors requires a reevaluation of what constitutes an “inventor” and how their intellectual property should be protected.
One potential solution could be assigning legal ownership of AI-generated inventions to the developers or organizations behind them, considering the innovative aspects and the responsibility and ethics involved in AI inventorship.
Global patent databases and innovative patent search tools can play a pivotal role in navigating this landscape by helping eliminate any “me-too” inventions and provide a wealth of content for AI systems to train their problem solving and reasoning capabilities that are needed for the Inventive thinking process.
Conclusion
While the debate surrounding AI as inventors is complex, it highlights the profound impact AI has on reshaping the world of invention. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and addressing accountability and ethical implications is necessary in updating patent laws to accommodate AI inventorship.
PatSeer, a patent analysis platform that offers robust search and analysis capabilities tailored to the evolving landscape of AI-generated inventions. With features like AI Recommender, Quick Summaries, and AI Relevance Scores, patent professionals can efficiently find relevant patents. PatSeer users can explore the nuances of AI-generated inventions that get registered globally, track legal precedents, and uncover global patent filing trends.






