Share
Share
Open Source vs. Software Patents: Can collaboration and Competition Coexist?
Although different in their ways, both open source and software patents are aimed at driving innovation. Technological innovation thrives on a fragile balance between open-sourced collaboration and competition led by protected software patents.
While open source encourages collaboration with freely accessible codebases or documentation, patents incentivize competition by granting exclusive rights to inventions for a limited period. Naturally, the question arises: Can these two opposite forces co-exist to encourage progress? Let’s find out.
Understanding Open Source
Open source refers to software or projects where the source code or information is made available to the public. This means that anyone can view, modify, and distribute it. The open-source movement began in the late 20th century. Major milestones include the creation of the GNU Project by Richard Stallman and the subsequent development of the Linux operating system. Open-source projects are led by the principles of collaboration, transparency, and community-driven development.
Key benefits of open-source inventions include:
- Collaboration: Contributors from around the world can add to the project database. Often, this leads to diverse perspectives and faster problem-solving.
- Transparency: Open access to source code and project documentation ensures that products can be scrutinized and improved by anyone.
- Rapid innovation: The collaborative nature accelerates the development process and the implementation of new features.
- Community-driven development: Projects are often maintained and enhanced by a dedicated community for continuous improvement and support.
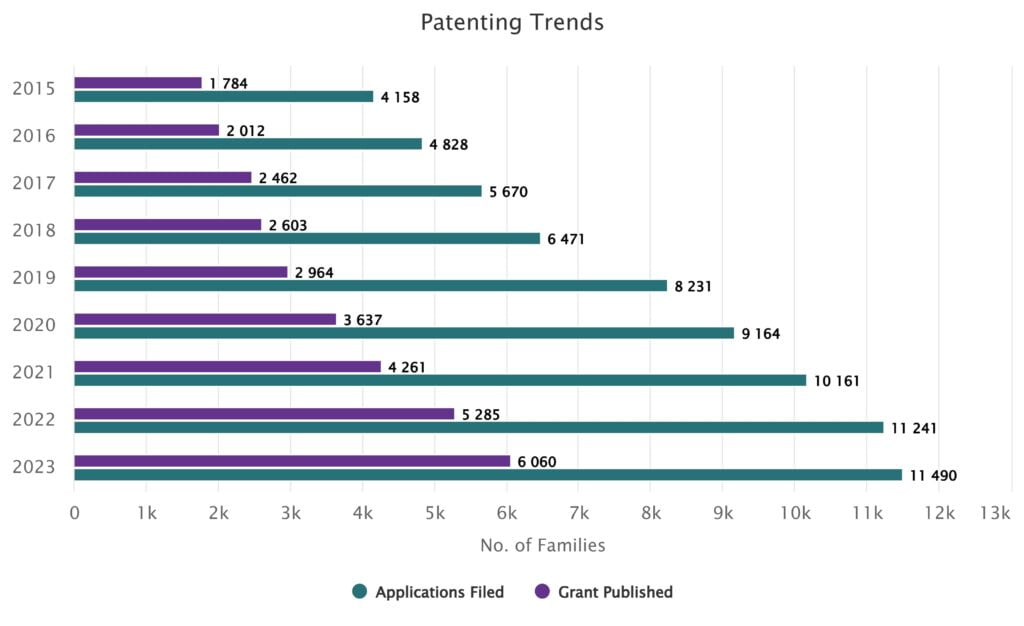
Figure: This chart shows a significant rise in the number of patent applications filed and granted related to software patents over the last decade.
Navigating the landscape of software patents necessitates comprehensive patent search and analytics, often aided by sophisticated patent research software, enabling innovators to stay abreast of the latest developments and potential conflicts. One crucial aspect of this is conducting an FTO Search (Freedom to Operate Search), a meticulous analysis of the intellectual property database to ascertain whether a product or service infringes on existing patents.
Contrasting Open Source and Software Patents
Open source promotes sharing the details of the project and collaborating on it. With public source code, anyone can contribute to the further development of the software. On the other hand, software patents offer exclusive rights to inventors; others are legally prevented from using, duplicating, or selling the patented invention without the permission of the patent owners. This prioritizes the incentivization of the software.
The Linux Project, Apache, and Mozilla Firefox are well-known examples of successful open-source projects. These projects have left a deep impact on their respective domains. On the other hand, products like Microsoft Windows or iOS are protected by patents. The inventors entirely control their use and commercialization.
Let’s glance at the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches in inspiring innovation:
| Open Source | Software Patents | ||
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Encourages collaborative innovation and problem solving | Leads to fragmentation | Provides extensive legal protection | Can stifle innovation in the market |
| Reduces operational costs | Potential security issues arise | Incentivized investment in research and development | Creates industry-wide monopolies |
| Readily available documentation | Absence of direct monetization | Enables monetization through licensing deals | Sometimes leads to costly legal battles |
| Open Source | |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Encourages collaborative innovation and problem solving | Leads to fragmentation |
| Reduces operational costs | Potential security issues arise |
| Readily available documentation | Absence of direct monetization |
| Software Patents | |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides extensive legal protection | Can stifle innovation in the market |
| Incentivized investment in research and development | Creates industry-wide monopolies |
| Enables monetization through licensing deals | Sometimes leads to costly legal battles |
Areas of Conflict
The junction of open source and software patents is particularly prone to legal and ethical concerns. Open-source developers may inadvertently infringe on existing patents, resulting in potentially expensive litigation that creates a chilling effect on further innovation. Ethically, the tension that exists between community-driven development and the need for exclusive rights brings about a division in the tech community, where some would find patents to be necessary protections and others would consider them barriers to progress.
Modern-day innovators must carefully weigh the pros and cons of open source and patents. Open-source work can align well with a developer’s philosophy of collaboration and transparency but may reduce one’s potential for protection and monetization of their work. Meanwhile, pursuing patents could provide legal protection and financial reward but may alienate a community that values openness. It’s often a delicate balancing act, requiring a nuanced understanding of both models.
Synergy between Open Source and Software Patents
Even though conflicts exist, there’s plenty of room for collaboration. For instance, Linux incorporates patented technologies from various companies. It led to Linux being a powerful and widely adopted platform. Similarly, the Android operating system is open source with a kernel based on Linux. Google uses patents to protect functionalities and control the platform’s direction.
To leverage both approaches, dual licensing is a great way. Companies can offer their software under both open-source and commercial licenses. The commercial license provides additional features and support for paying customers. An open-core model is also gaining widespread adoption, in which companies release the core functionalities of their software as open source while keeping certain advanced features proprietary.
Companies like Red Hat use dual licensing to offer their core operating system (CentOS) for free while generating revenue through the commercially licensed Red Hat Enterprise Linux. The open-core model is used by MongoDB, which provides a free, open-source community edition and a commercially licensed enterprise version with additional features and support.
Impact on Different Industries
In the software industry, open source has turned into a dominant driver of innovation, mostly in the development of operating systems and web development. However, complicated and cost-intensive innovations in the biotechnology sector are heavily reliant on patents, although open-source projects in genomics are emerging. The electronics sector often sees a combination of open hardware and software with patented technologies, mainly around embedded systems.
Companies like Google and Red Hat have already combined open-source strategies with a robust patent portfolio in such a way that it has allowed for innovation while defending against competitors. For instance, Google’s Android operating system is open source, and it has several patents related to mobile technology that let it defend its innovations while creating a vibrant developer community. Red Hat, an open-source software pioneer, holds patents but only uses them in ‘defensive patenting,’ only promising to assert them if attacked. These are just a few examples of how companies may steer their way around open source and patents on their way to success.
Collaboration and competition work hand in hand to drive innovation in today’s technological world. Open source and software patents serve quite distinct purposes in encouraging technical innovation. Appreciating these dynamics and embracing their potential synergy can create a vibrant and inclusive future for innovation. The strategic use of patent search and analytics tools and the development of advanced AI classifiers for patent analysis are essential in navigating this complex landscape, fostering a balance between open collaboration and incentivized competition for a brighter technological future.
PatSeer, an AI-powered patent search and analysis platform, transforms how businesses and innovators manage IP. In the complex interplay between open-source collaboration and patent-driven competition, PatSeer is a valuable tool that helps users navigate patent landscapes with confidence. Utilizing advanced AI capabilities, PatSeer efficiently uncovers critical prior art, assesses patentability, and monitors industry trends, saving both time and resources. Its comprehensive reports provide decision-makers with actionable insights, fostering innovation while mitigating legal risks.